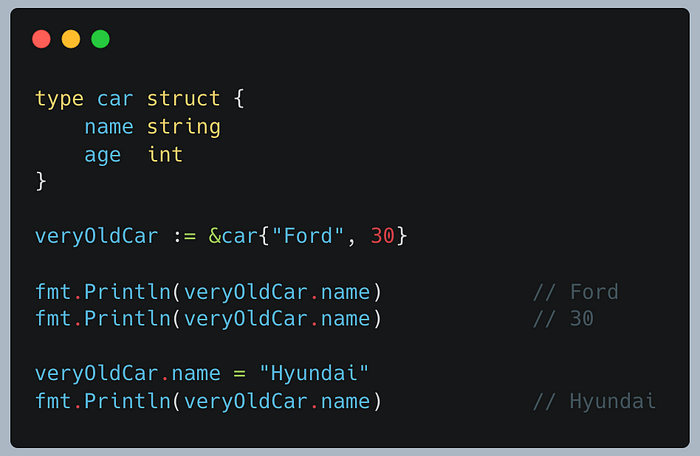
Given the example below, for a struct named “car”:

We can then create a function that acts as a constructor, creating a new instantiated car struct for us:
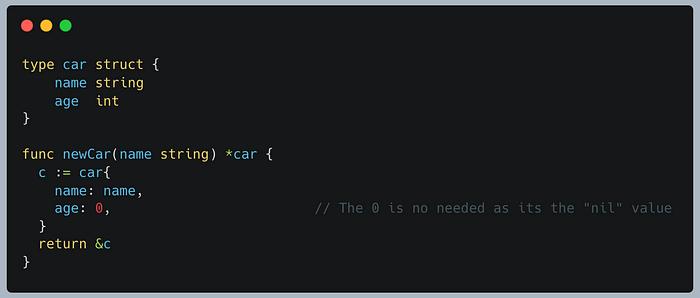
The function: “newCar” takes in a name of type string, and returns us a new car, with an age of 0 (notice the comment).
When instantiating a new “car” struct, you don't actually need to give the name of the parameters, like “name” and “age”, though it's recommended to show explicitly which parameter the value is assigned to:

As described in the previous post about pointers you can also pass a pointer to the newly created car struct:

Then when you want to access the values stored in a struct you use the dot notation:
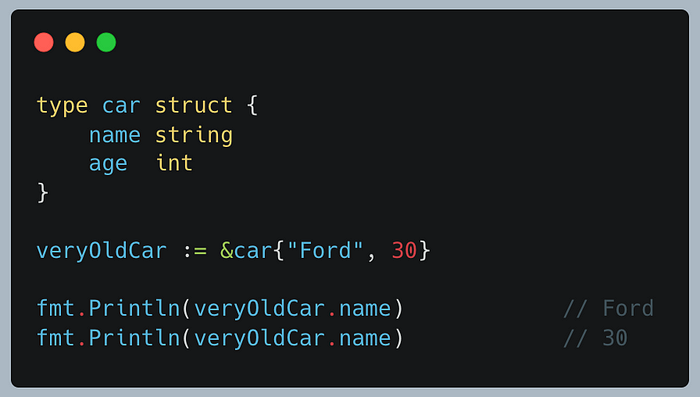
Not only can you access the values stored in a struct, but you can also change/update these values: